TOPIC 3: BUSINESS PLANNING
The business planning processSources of planning ideas
|
Forecasting
|
Biz Plan by Philip Wilson (CC BY-ND 4.0)
Business plans - introduction
The image above is basically what a business plan is about (even if it misspells analysis). The purpose of a business plan is to tell readers about your business idea and the strategies that will make it successful. It's also to go through a process so that the founders themselves can determine if the business is successful. Potential investors and loan providers usually want to view a business plan before they commit any finance. If you watch Shark Tank you will soon notice that the 'sharks' want to be pitched a plan and they are obviously provided with a printed business plan before the show starts. They won't invest if the plan isn't good enough.
If you Google 'business plans' you will find a wide range of points that various business plans can have and many templates. At the top of this page is the list of points the syllabus writers believe are important for a business plan.
For examples of business plans, see FormSwift's Sample Business Plans. For more examples and a template see growthink's Business Plan Template and Guide.
If you Google 'business plans' you will find a wide range of points that various business plans can have and many templates. At the top of this page is the list of points the syllabus writers believe are important for a business plan.
For examples of business plans, see FormSwift's Sample Business Plans. For more examples and a template see growthink's Business Plan Template and Guide.
Sources of planning ideas
When starting a business the owners/manager need to thoroughly understand what the business itself is about and the environment (market) in which it operates. In other words, knowing what situation the business is in. To gain this knowledge a situational analysis is conducted. It is very similar to an army unit being dropped into a war zone. A situational analysis allows the army to assess the resources they have, the resources they are lacking and now need, what threats surround them and what opportunities they have to gain ground. A favourite tool for conducting a situational analysis in the SWOT analysis. To conduct a situational analysis research must be conducted, questions asked of many people including:
- industry associations
- lawyers/solicitors
- accountants
- successful business owners
- marketing experts
- potential customers
- potential staff
- potential suppliers
Business plan competitions
TASK:
This whole topic can be completed as a project.
In groups or as individuals, you are going to prepare a business plan.
There are two competitions you can enter with your business plan: These websites also have templates of business plans.
Whatever template you choose to use, for syllabus purposes it needs to include:
This whole topic can be completed as a project.
In groups or as individuals, you are going to prepare a business plan.
There are two competitions you can enter with your business plan: These websites also have templates of business plans.
Whatever template you choose to use, for syllabus purposes it needs to include:
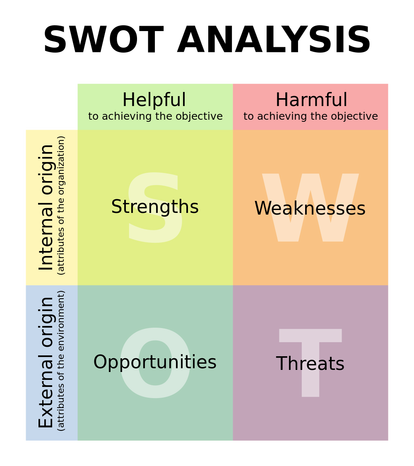
- SWOT Analysis
- Vision, goals and/or objectives
- Organisation of the Key Business Functions (Operations, Marketing, Finance and HR)
- Break-even analysis
- Cash-flow projections
By Xhienne (SWOT pt.svg) [CC BY-SA 2.5], via Wikimedia Commons
READ:
For a good overview see SWOT analysis by MindTools.
For a more comprehensive guide see FormSwift's Guide to SWOT Analysis.
For a good overview see SWOT analysis by MindTools.
For a more comprehensive guide see FormSwift's Guide to SWOT Analysis.
Visions, goals and/or objectives
It is important to set a vision and business goals/objectives to help the business strive for long-term growth.
READ: Business Plans Include Vision, Mission Statement, and Objectives, Don't They? What's the Difference? (allBusiness)
READ: Business Plans Include Vision, Mission Statement, and Objectives, Don't They? What's the Difference? (allBusiness)
Organising resources
A business plan needs to outline the key business functions of the business.
Operations Plan
The process by which the business prepares, produces or obtains the goods and services, including decisions made regarding:
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan outlines the strategies and include:
Finance/Financial Forecasts
In order to conduct business activities and monitor performance, financial objectives need to be set. Financial information to be provided should include:
Human Resources Plan
This section outlines the people needed to run the business as part of the HR Cycle (acquisition, development, maintenance, separation):
Operations Plan
The process by which the business prepares, produces or obtains the goods and services, including decisions made regarding:
- Materials – inventory (items bought for resale), raw materials used in production
- Suppliers – who to use considering costs, transport, reliability, etc
- Facilities – buildings, machinery, layout of operations, etc
- Quality management – monitoring of quality
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan outlines the strategies and include:
- Identification of the target market using market research
- Marketing mix
- Product – branding, packaging
- Price - pricing strategies (skimming, penetration, loss leaders, price points)
- Promotion - advertising, , sales promotions, public relations, etc
- Place – distribution channels
Finance/Financial Forecasts
In order to conduct business activities and monitor performance, financial objectives need to be set. Financial information to be provided should include:
- Start-up (establishment) costs
- Sources of finance (debt/equity)
- Projected cash flow statement
- Projected income statement
- Balance sheet forecast
Human Resources Plan
This section outlines the people needed to run the business as part of the HR Cycle (acquisition, development, maintenance, separation):
- Management roles
- Required staff
- Organisation of teams (organisation chart)
- Skills required of staff for the various roles
- How staff are to be recruited, trained and developed
- Wages/salaries
Forecasting
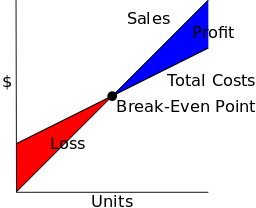
Break-even analysis
A business breaks even when money earned from sales equals what it has cost to make the sales. There is no profit and no loss. It lets you know exactly how much you must sell at the present level of costs in order to avoid making a loss and it can be used regularly to check the progress of your business by comparing sales achieved with the break-even point.
Variable Costs are costs that are directly related to the volume of sales. This means they increase as output rises and include the raw materials used to make the product.
Fixed Costs are those costs that continue regardless of how much you produce. These can be made up of such expenses as rent, depreciation, telephone accounts and insurance.
Total Revenue/Sales is determined by multiplying the quantity sold by the sales price (price x quantity)
The break-even point can be calculated by using the formula:
Break-even point = total fixed costs
Unit price – variable costs per unit
A business breaks even when money earned from sales equals what it has cost to make the sales. There is no profit and no loss. It lets you know exactly how much you must sell at the present level of costs in order to avoid making a loss and it can be used regularly to check the progress of your business by comparing sales achieved with the break-even point.
Variable Costs are costs that are directly related to the volume of sales. This means they increase as output rises and include the raw materials used to make the product.
Fixed Costs are those costs that continue regardless of how much you produce. These can be made up of such expenses as rent, depreciation, telephone accounts and insurance.
Total Revenue/Sales is determined by multiplying the quantity sold by the sales price (price x quantity)
The break-even point can be calculated by using the formula:
Break-even point = total fixed costs
Unit price – variable costs per unit
READ: Section 5 on this SimpleStudies webpage.
TASK: Luke's Candle Shop Exercise (written task) and Wraps Sunglasses Exercise (Excel)
Cash flow projections
READ: NAB's guide to cash flow forecasts and Are you on top of your cash flow forecast? (smh).
TASK: Luke's Candle Shop Exercise (written task) and Wraps Sunglasses Exercise (Excel)
Cash flow projections
READ: NAB's guide to cash flow forecasts and Are you on top of your cash flow forecast? (smh).
Monitoring, evaluations and taking corrective action
Your business plan should be a living document that is reviewed and updated regularly. Using your business plan as an operating guide for your business will help you to make the most of new opportunities, identify potential risks, and act before they occur.
www.business.qld.gov.au/starting-business/planning/turn-into-business/business-plan
READ: How to monitor and control your business plan (Chron) and What is a sales analysis report? (also Chron)